LPU’s Innovative Water Reuse Strategy for Sustainability
Water reuse and recycle is the vital step towards water conservation. LPU has taken leading initiatives in this aspect. The sewage water has been segregated into black water and grey water and managed individually. The university employs an effective wastewater management strategy that distinguishes between greywater and black water to optimize resource use and environmental sustainability. Greywater, which includes wastewater from sinks, showers, and laundry, undergoes nominal treatment before being repurposed for landscape gardening and toilet flushing. In contrast, black water, which consists of wastewater from toilets, undergoes a rigorous treatment process to ensure it meets the effluent discharge standards required for safe release into the environment. This comprehensive treatment ensures that harmful contaminants are removed, safeguarding public health and protecting local ecosystems. Recognizing that conventional wastewater treatment can be energy-intensive and may not always effectively address all types of wastewater generated in an institutional setting, the university is continuously exploring innovative methods to enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of its treatment processes. By prioritizing both greywater reuse and advanced black water treatment, the university exemplifies a holistic approach to wastewater management that prioritizes sustainability, resource conservation, and environmental protection, setting a standard for responsible practices in higher education. Hence flexible wastewater treatment technologies ranging from conventional to advance has been installed and operated in order to treat all type of wastewater generated within the premises most effectively and energy efficient way. Gradually but steadily through these initiative, LPU is paving towards energy effective waste treatment and zero liquid discharge.
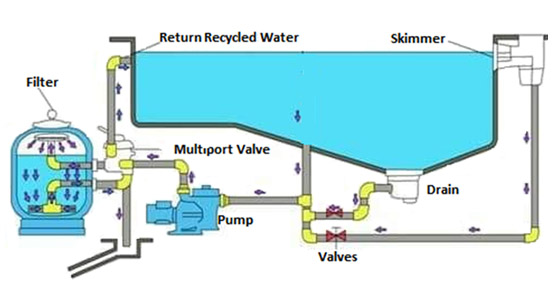
LPU’s Approach to Reusing Swimming Pool Water
Lovely Professional University’s approach to reusing swimming pool water. By maintaining stringent sanitation protocols and addressing challenges like calcium buildup, LPU ensures a safe and enjoyable swimming experience while significantly reducing water waste. This model can serve as an inspiration for other institutions and communities aiming to adopt sustainable water management practices.
The primary goal of these water management practices is to reduce impurities in the pool water to a safe level, allowing for its continuous reuse. The benefits of LPU’s approach include:
- Water Conservation: By recycling pool water, LPU significantly conserves water, aligning with environmental sustainability goals.
- Cost Savings: Reduced need for fresh water lowers operational costs associated with pool maintenance.
- Enhanced Sustainability: Implementing such advanced water management systems demonstrates LPU’s commitment to sustainability and environmental management.
Sustainable Pool Water Management
Recycling Pool Water and reusing it in swimming pool water at Lovely Professional University: A Model for Water Conservation. Lovely Professional University (LPU) has recognized the critical importance of water conservation and has implemented innovative strategies to minimize water waste, particularly in the maintenance of its swimming pools. The university has introduced restrictions and practices aimed at recycling pool water rather than draining and refilling it, thereby setting a precedent for sustainable water management.
A significant measure adopted by LPU is the use of Reverse Osmosis (RO) systems for pool water treatment. This advanced filtration technology enables the university to maintain clean and safe pool water without the need for frequent draining. Here’s how the RO system contributes to water conservation:- High-Pressure Filtration: The RO system uses high pressure to force pool water through a fine semipermeable membrane. This membrane effectively retains salts, cyanuric acid, calcium, and other impurities.
- Water Reuse: Clean water is returned to the pool, ensuring that the water remains safe and pleasant for swimmers. The separated contaminants and dirty water are then pumped out and managed appropriately.
- Reduction of Water Waste: By recycling the pool water through the RO system, LPU significantly reduces the volume of water that would otherwise be wasted through draining and refilling.
To ensure that recycled pool water remains safe and hygienic, LPU employs a comprehensive sanitation protocol:
- Filtration: Regular filtering removes particulate matter and debris from the water.
- Chlorination: Chlorine is used to disinfect the water, killing bacteria, microbes, and other potential contaminants.
- pH Level Maintenance: Maintaining the correct pH level is crucial to prevent skin irritation and to ensure the effectiveness of chlorine. LPU monitors and adjusts the pH levels meticulously.

Strategic Management of Sustainable Water Storage at the University
The university has made significant strides in sustainable water storage management through its initiatives to capture, store, and utilize treated water across campus. One of the most impactful efforts is the installation of three large water storage tanks, each with a capacity of 25,000 liters, located at the Sports Fields. These tanks are designed to collect and store treated water, which is used to irrigate the fields, reducing reliance on municipal water supplies and conserving valuable freshwater resources. This system ensures that the sports fields remain well-maintained year-round, even during periods of low rainfall or water restrictions, while minimizing the environmental footprint of campus operations.
The water storage management initiative not only supports the university's commitment to sustainability but also demonstrates how institutions can effectively manage natural resources to meet their water needs. By capturing treated water and putting it to productive use, this forward-thinking approach aligns with the university's broader goals of environmental stewardship, resource conservation, and the creation of a resilient, self-sustaining campus.

Recycled Water used to Powers Air-Conditioning
Recycled water at 1 Central Courtyard is used for the air-conditioning cooling towers, along with irrigation of the gardens in the precinct.
Here are some additional details about the university's water reuse practices:

Irrigation and Horticulture:
Treated water from the STPs is primarily used for irrigation and horticulture purposes, including watering plants like Eucalyptus and other vegetation across the campus. This demonstrates a sustainable approach to maintaining greenery on the campus while conserving freshwater resources.

Flushing:
The university has adopted an innovative approach to water conservation by utilizing treated water for dual purposes, including flushing toilets. This practice not only reduces the demand for fresh potable water but also ensures that water is used efficiently throughout the campus. By repurposing treated water for non-potable uses such as toilet flushing, the university significantly decreases water wastage, contributing to a more sustainable and responsible water management system. This initiative supports the broader goal of conserving precious freshwater resources, especially in regions where water scarcity is a growing concern. The dual use of treated water also aligns with the university's commitment to environmental stewardship by reducing the environmental impact of campus operations. Through this initiative, the university fosters a culture of sustainability among students, staff, and visitors, encouraging mindful water consumption while demonstrating how resourceful practices can lead to meaningful change. The integration of treated water for toilet flushing is a practical and effective solution that reinforces the university’s dedication to responsible water use and sustainable campus development.. A dedicated pipe-line that it's a 9-inch diameter pipeline, extending over a kilometer in length. This infrastructure allows for efficient and widespread use of the treated water.

Sludge Utilization:
The sludge obtained as a byproduct of the water treatment process is used as manure in horticulture. This practice showcases the university's commitment to minimizing waste and recycling resources as well as this practice ensures that waste materials are not discarded but instead transformed into valuable resources that support the growth of plants and the overall health of campus gardens and green spaces. By using treated sludge as organic manure, the university minimizes its environmental footprint, reducing the amount of waste sent to landfills and closing the loop in its resource management system. This approach also enriches the soil, promoting the health and vitality of the campus landscape while reducing the need for synthetic fertilizers, which can have harmful environmental impacts. The use of sludge as manure exemplifies the university's dedication to creating a sustainable, eco-friendly campus where resources are thoughtfully recycled and reused. This initiative serves as a practical example of how waste can be converted into a beneficial product, furthering the university's mission to minimize waste, promote environmental stewardship, and foster a culture of sustainability among the campus community.

Additional STPs:
The presence of smaller sewage treatment plants (STPs) with capacities of 10,000 liters each at the Main University Playgrounds and Agriculture farmland further contributes to water conservation and efficient utilization. These additional STPs help manage wastewater effectively in these specific areas.

Utilization of treated water:
Treated water from the 5 MLD Sewage Treatment Plant plays a key role in sustainability by treating wastewater for reuse in a variety of applications, including toilet flushing, gardening, drip irrigation, horticulture, agriculture, and poly-house farming. This efficient system ensures that treated water is repurposed for essential campus functions, reducing reliance on fresh water and promoting responsible resource management. Through this initiative, the university demonstrates its commitment to environmental conservation and sustainable water use practices.It transforms the campus into a green and environmentally friendly oasis, promoting a healthy and inspiring environment for students and faculty.
Preventing Entry of Polluted Water:
Integrated Loft tanks are installed at wastewater outlets, following guidelines from the Biomedical Waste Management Rules (BMWM) of 2016. These loft tanks are utilized for the primary treatment of wastewater, employing a hypo solution to neutralize contaminants before the water enters the university's system. This process prevents the entry of polluted water into the broader water infrastructure, ensuring that water quality is maintained across campus. By following the Biomedical Waste Management Rules (BMWM) of 2016, the university safeguards its water resources and supports its overall sustainability and environmental stewardship goals.This practice helps maintain water quality.
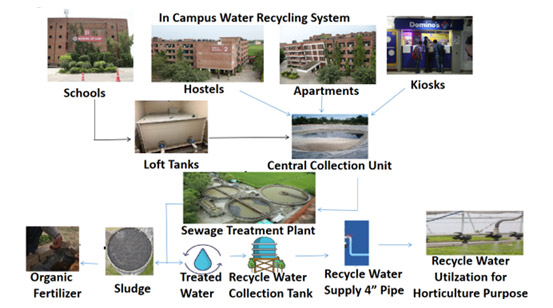
LPU’s Comprehensive Water Reuse Practices for Sustainability:
Lovely Professional University (LPU) has integrated comprehensive water reuse practices, aligned with Sustainable Development Goal 6 (SDG 6), to reduce reliance on freshwater sources and mitigate environmental impacts. The Division of Waste Management Landscape Architecture and Environment is responsible for measuring and managing the volume of reused water treated from wastewater across the campus. This ensures efficient water use for various university operations while safeguarding surrounding ecosystems.

Digital Meters Monitor Sustainable Water Extraction at LPU
In addition, there are 32 Digital water meters, installed on each of these waters bore, to measure the volume of water extracted from the ground, using sustainable water extraction technologies.
Water Reuse Measurement:- LPU fresh water extracted approximately 4,600 cubic meters of water per day, measured by pumping systems and water meters installed across academic buildings, dormitories, research facilities, and other university infrastructure.
- The university treats waste water approximately 2,500–4,000 cubic meters of wastewater daily, as recorded by flow meters. This treated water is verified to be free from chemical contaminants before reuse.
- Irrigation and Landscaping:
- Sprinkler systems are used for watering plants and maintaining landscapes across campus, ensuring efficient water usage. Reused water supports aquaculture activities on campus.
- Vehicle Washing and Road Cleaning: Recycled water is used for cleaning university vehicles and maintaining road cleanliness on campus.
- Cooling Systems: Treated wastewater is utilized in cooling systems, particularly to lower the temperature of waste incinerators, ensuring optimal room temperature control.
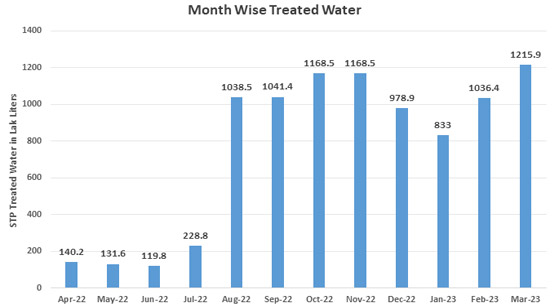
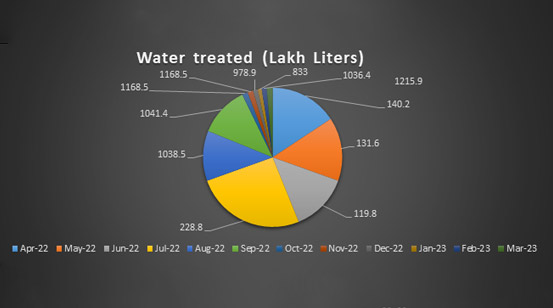
Regular Water Measurement Practices
By regularly measuring the quantity of water reused on campus, LPU showcases a proactive approach to sustainability and responsible resource management. This practice allows the university to track its water conservation efforts, ensuring that resources are being used efficiently and that water waste is minimized. By carefully monitoring the amount of recycled water, LPU is able to make data-driven decisions that optimize water usage for various purposes, such as irrigation, flushing, and landscaping. This not only conserves freshwater supplies but also reduces the university's environmental footprint, aligning with its commitment to sustainable practices. Furthermore, this approach benefits both the university community and the surrounding environment, as responsible water management supports the health of local ecosystems and reduces the strain on public water systems. By taking such measures, LPU leads by example, fostering a culture of sustainability on campus while demonstrating the importance of resource conservation to students, staff, and the broader community. This ongoing commitment to monitoring and optimizing water reuse reflects LPU’s dedication to protecting the environment and promoting long-term sustainability.
Furthermore, the university's dedication to water treatment and reuse further exemplifies its commitment to sustainable practices. By treating and recycling water, the institution not only conserves this valuable resource but also reduces the strain on local water supplies, contributing to the overall well-being of the surrounding community. These sustainable water management practices serve as a model for other educational institutions and organizations looking to prioritize environmental responsibility and water conservation.
Clean water and sanitation annual report
The attached Annual Report provides an overview of LPU comprehensive water reuse practices, a cornerstone of its sustainability efforts aligned with SDG 6. The university focuses on water conservation, resource management, and environmental stewardship through various initiatives. Treated water from the university's Sewage Treatment Plants (STPs) is repurposed for irrigation, landscaping, and toilet flushing, significantly reducing reliance on potable water. The university also uses treated water for cooling systems, while sludge byproducts are utilized as organic manure, contributing to campus sustainability. LPU’s robust water reuse policy encompasses wastewater treatment, recycling, and water-saving technologies, supported by extensive infrastructure, including a dedicated 9-inch pipeline for water distribution. Through collaboration with national and international bodies, LPU continues to enhance its water management practices, demonstrating leadership in sustainable water use and reinforcing its commitment to water security.
Click here
Guidelines on water use and its discharge in campus
INTRODUCTION
Water is a blessing for human life and natural water resources are being exhausted to meet its increasing requirement since it doesn’t have a substitute. Therefore, recycling or reuse of water is important for sustainable development and to ensure the availability of clean water to future generations
Lovely Professional University thus has contributed in various ways and numerous efforts by initiating integrated efforts to ensure adequate infrastructure, processes and guidelines, in line with Government, for providing the sufficient and sustainable water facilities within Campus. Comprehensive and continuous efforts are made by the University to facilitate safe and affordable drinking water. In addition, efforts for the treatment of waste water produced in Campus and maximization its use also been made.
SCOPE
The scope of these guidelines is to provide a roadmap and guidelines with background and a broad conceptual framework for planning/implementing strategies for sustainable development that includes water management, conservation of water, water security and educational programs for increasing awareness.
OBJECTIVES
- To maximize the judicious use of water in the campus.
- To increase the awareness among campus population and nearby localities for the sustainable use and reuse/recycle of water
- To ensure the 24 X 7 availability of free and clean drinking water to all inside the campus.
- To ensure the sewage treatment as per the prevailing norms.
- To contribute towards upliftment of ground water table level.
- To establish and maintain water quality standards through pretreatment before it discharge that safeguard the ecological integrity of the water bodies.
GUIDELINES ON WATER USE ON CAMPUS
University must make dedicated efforts towards the provision of fresh water facilities as well as the treatment of water. For achieving clean water and sanitation, the University must introduce various processes and policies such as:+
4.1 Access to Free and Clean Water
- University must provide clean and free drinking water facility to the entire Campus population.
- There must be routine water audits and water quality checks from accredited or certified agency, to ensure the quality of water.
- The water filters must be cleaned/serviced regularly to ensure the un-interrupted supply of clean and safe water, from certified service providers.
- To ensure the minimum wastage of clean water, the automatic sensor-based urinal pot, semi-automatic minimum water usage push button taps, two button toilet flush water tanks, water saving spray jet nozzles etc. must be installed in Campus.
- The volume of water extracted from underground, aquifers, lakes, or any natural water body, for this purpose, must be recorded using water meters across whole University.
- For ensuring the adequate supply of clean water, University must organize awareness programs, seminars, workshops, plays campaigns etc. must be organized from time to time both within and outside the University campus, focusing on key indicators of clean water, water reuse, water security and management.
- University should emphasize the importance of conservation of water, water management, by implementing these strategies in the curriculum and daily activities of the university for sustainable development.
- University must ensure the proper utilization of overhead tanks for storing water and using it for drip irrigation, horticulture and agriculture.
- University must contribute towards the global mission of “Clean Water” by co- operating with local, regional, national or international bodies/NGOs/Governmental agencies, etc. to work on water security.
- A separate water treatment plant (Reverse Osmosis plant) can be installed for each block for supply of purified water.
- All the waste discharge from university must be pretreated to remove any hazardous and toxic material before discharge to environmental bodies. The treated water can be tested timely to ensure the quality of water being discharge and meet the prescribed standards before its discharge.
4.2 Treatment of Waste water
- Adequate number of Sewage Treatment Plants (STPs) must be installed at various location inside the Campus to treat the waste water.
- University will direct its efforts to optimize the capacity of the STPs for treating the waste water.
- University must focus on utilization of treated water for flushing the toilets.
- The waste water produced in the Campus must be disposed-off to the surroundings only after pretreatment of the same. This must be as per the Punjab Pollution Control Board and/or Central Pollution Control Board guidelines to protect human health and healthy ecosystems (both aquatic i.
e. freshwater as well as marine restrial ecosystems). - The treated water can be used for irrigation purposes, toilet cleaning, etc. and must take efforts to use gray water.
- The waste water expected to be rich in microbial content must be disposed-off after pretreatment as per Bio Medical Waste Management guidelines laid down by Govt. of India.
- The quality of treated water must also be examined on a timely basis to ensure the proper functioning of Sewage Treatment Plants.
- The sewage treated water can be used for irrigation of trees, using The Karnal Technology.
- University must ensure that the discharge water may not affect the aquatic ecosystem.
4.3 Rain water harvesting
- University must provide rain-water harvesting bores within the Campus to ensure the recycling of rain water and contribute towards sustainable development.
- The volume of rain water harvested must be measured using water meters and the consequent effect of ground water recharging must be monitored.
- University must ensure the prevention of polluted water, harmful water or any polluted water from accidents and incidents in surroundings/University to clean water and must take steps in this direction.
- The collection of rain water must be collected through surface runoff collection from terraces that is connected to a rainwater recharge well by a pipe line.
- Ensure the discharged rainwater does not pose health or safety risks to the public, environment and water bodies.
4.4 Other Initiatives
University must take following initiatives for the water use with in the campus:
- Implement building standards to minimize water usage and maximize water reuse. The quantity of reused water must be recorded.
- Implement water conservation method like drip irrigation, leakage repairs, and condensate recovery.
- Implementation of water recycling techniques including dissolved air flotation, biological treatment, granular activated carbon, softening, disinfection, deionization and filtration etc.
- Initiate plantation such that the plants (Drought resistant plants) require lesser water for growth and sustenance.
- Initiate in-designing of the campus roads with saucer drain section to collect water from the road network and from the paver’s walkways.
- Initiate by installing solar water pumps to run the water pumping system in the campus.
- Implementation of water filling in overhead water tanks with a time-controlled pumping system at individual campus buildings.
- University must carry out collaborative research to address issues on aquatic (freshwater and marine) ecosystem.
- Compliance with government guidelines for the water discharge to protect the ecosystem.
- Ensure the 24 x 7 supply of quality potable water.
- In order to minimize water usage, students are encouraged to use buckets instead of showers.
- University increase vegetation cover in order to prevent top soil erosion.
- Prioritize source reduction, recycling, and treatment before water discharge.
- Avoid discharging near sensitive ecosystems, wetlands, or water bodies with fragile habitats.
These guidelines must be reviewed periodically considering the data stats and analysis to overcome the system lags and ensure the sustainable supply of clean water.